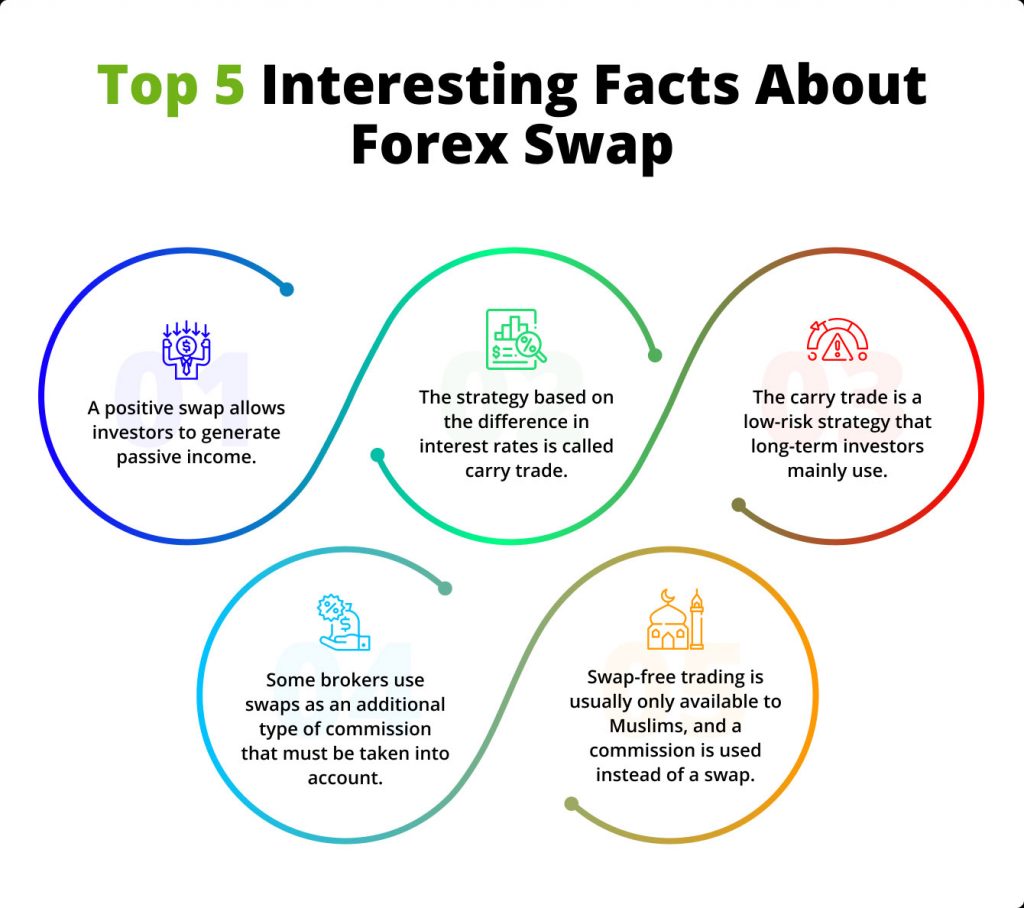
What is Swap Market in Forex Trading?

![]()
What is the Forex Swap Market and How Does it Affect My Trading?
Foreign currency swap (Swap Market), known as an forex swap, is an agreement between two foreign parties to exchange currencies. Arrangement comprises exchanging principal and interest on one loan for principal and interest payments on another loan of similar amount.
A party borrows currency from a third party while simultaneously lending that party another currency.
Whats Swap in Forex ?
A Forex swaps originally adopted by the World Bank in 1981 in order to obtain German marks and Swiss francs. On loans with durations of up to ten years, this type of swap is possible. During the term of a currency swap, each party continues to pay interest on the swapped principal amounts.
When swap completed, principle amounts re-exchanged at a pre-determined rate or the spot rate. In a fixed-for-fixed currency swap, fixed interest payments exchanged for variable interest payments in one currency.
What is a Currency Swap in Swap Market and How Does It Work?
The counter-parties in a currency swap, also known as an FX swap, exchange predetermined amounts in two currencies. One party may receive 100 million British pounds (GBP), while the other may receive $125 million. This equates to a 1.25 GBP/USD exchange rate.
To complete the transaction, they will switch at the end of the agreement, either at the original exchange rate or at a pre-agreed rate.
Example From the Real World
Consider a company that has US dollars but needs British pounds to establish a new venture in the United Kingdom.In the meanwhile, a British company needs US capital to make a US investment.
They meet through their banks and reach an arrangement to get the money they need without having to go to a foreign bank for a loan, which would almost definitely come with higher interest rates and a heavier debt load. Currency swaps not required to recorded on a company’s balance sheet, although loans.
Learning about Foreign Exchange Swaps in Swap Market
Both parties must own a currency and require the counterparty’s currency in order for a foreign exchange swap to be successful. Two “legs” are present:
The initial leg involves a deal at the current spot rate. Amounts of equal value exchanged between the parties at the current exchange rate. The exchange rate at the start date is the spot rate.
A transaction at the predetermined forward rate at maturity makes up the second leg. Each party receives the currency they lent and returns the currency they borrowed after exchanging quantities once again.
The exchange rate for a future transaction is known as the “forward rate,” and it is often decided by the parties based on their estimates for the relative appreciation or depreciation of the currencies. Expectations are based on the interest rates that the different currencies are willing to give, as shown by interest rate parity. In order to offset anticipated depreciation against currency B, currency A may provide a higher interest rate, and vice versa.
Formula for Interest Rate Parity
Swaps of foreign currencies can be used to borrow or lend money without taking out a cross-border loan. By securing the forward rate and confirming the future payment, it also avoids the danger of currency fluctuations.


Visit us on: www.milliva.com





What is Forward market in forex?
14th Jul 2022[…] Swaps used to price and execute interbank forward foreign currency markets. This means that currency A acquired in exchange for currency B for delivery on the spot date at the market rate at the time of the transaction. Currency A sold vs. At maturity, currency B is worth the original spot rate plus or minus the forward points; this price decided when the swap initiated. […]