Main Factors Affecting Forex Market

![]()
With buyers and sellers from all over the world taking part in trades worth trillions of dollars every day, forex is a true global marketplace. Given the increased globalization of foreign currency trading, macroeconomic events from all around the world now factors affecting forex market more than ever. Although they are an excellent place to start, traders are no longer need to stick with widely used currencies. The currency exchange rate is one of the most significant drivers of a country’s relative degree of economic health, along with variables like interest rates and inflation.
Every free market economy in the world depends on trade, which significantly influenced by exchange rates. Exchange rates are among the economic indicators that most closely monitored, studied, and subject to political manipulation because of this. However, exchange rates are also important on a smaller scale since they affect the portfolio’s real return. Here, we examine some of the main factors affecting forex market currency rates.
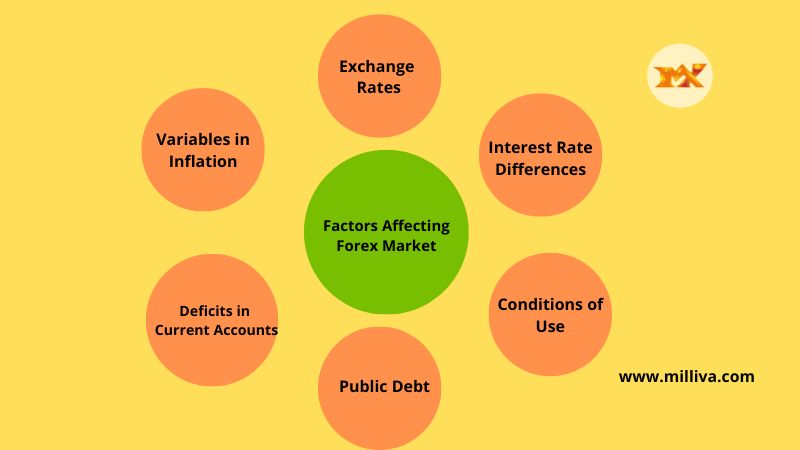
Top 6 factors affecting forex market
Introduction to Exchange Rates
Before examining these forces, it is important to consider how changes in the exchange rate impact a country’s international trade connections. A currency with a higher value makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive in overseas markets. A country’s exports are less expensive in foreign markets and its imports are more expensive when its currency depreciated. A country’s trade balance predicted to get worse with a higher exchange rate while getting better with a lower one.
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates
Exchange rates influenced by many things. Many of these elements have to do with how the two nations’ trading relations. Keep in mind that exchange rates are based on a comparison of the currencies of two different nations.
Some of the main factors affecting the exchange rate between two countries include the ones listed below. The relative relevance of these factors is up for question, just like it is with many other aspects of economics. Therefore take note that they not listed in any particular order.
Variables in Inflation
A nation with a historically low inflation rate typically has a growing currency value as its purchasing power rises in relation to other currencies. Japan, Germany, and Switzerland were among the nations with low inflation in the second half of the 20th century; the United States and Canada only subsequently attained this level of low inflation.
The currencies of those nations with higher inflation often depreciate relative to those of their trading partners. Higher interest rates are typically accompanied by this as well.
Interest Rate Differences
Exchange rates, inflation, and interest rates all have a close relationship. Central banks control inflation and exchange rates through adjusting interest rates, which has an effect on both inflation and the value of currencies. An economy with higher interest rates provides lenders with a larger return compared to other nations. As a result, higher interest rates draw in foreign investment and drive up the value of the currency. However, the effect of higher interest rates is lessened if inflation in the nation is significantly higher than in other nations or if other factors contribute to the depreciation of the currency. Lower interest rates tend to cause exchange rates to rise, which is the opposite of the link that obtains for decreasing interest rates.
Deficits in Current Accounts
The balance of trade between a country and its trading partners, which includes all payments for goods, services, interest, and dividends, is known as the current account. A negative current account balance indicates that a nation borrows money from abroad to cover the deficit, indicating that it spends more on international trade than it brings in. In other words, the nation needs more foreign currency than it generates through export sales, and it produces more of it than foreigners are willing to pay for it. As local goods and services become affordable enough for foreign customers and foreign assets become too expensive to produce revenue for domestic interests, the country’s exchange rate declines as a result of the excessive demand for foreign money.
Public Debt
Large-scale deficit financing will used by nations to pay for public projects and governmental spending. While this activity boosts the domestic economy, international investors are less likely to invest in countries with huge public deficits and debts. The cause? A large debt promotes inflation, and if inflation is strong, the loan will eventually be serviced and repaid with real dollars that are less expensive.
In the worst case, a government may issue currency to partially pay off a big debt, but expanding the money supply invariably results in inflation.
Additionally, a government must increase the number of securities available for sale to foreigners in order to lower the price of those assets if it is unable to finance its deficit through domestic methods (selling domestic bonds, expanding the money supply). Finally, if foreign investors think the nation might default on its debts, a high debt may worry them. If there is a high chance of default, foreigners will be less eager to purchase securities denominated in that currency. Because of this, the country’s debt rating—as established, for instance, by Moody’s or Standard & Poor’s—is a significant factor in determining its exchange rate.
Conditions of Use
The terms of trade, which compare export prices to import prices, has an impact on current accounts and the balance of payments. A country’s terms of trade have improved favourably if the price of its exports grows faster than the price of its imports. Growing terms of commerce indicate increased demand for the nation’s exports. In turn, this leads to a rise in export earnings, which raises the value of the local currency and increases demand for it. The value of the currency will fall in comparison to its trade partners if the price of exports increases at a slower rate than the price of imports.
Excellent Economic Performance
Foreign investors invariably look for stable nations with robust economies to place their money in. A nation with such favorable characteristics will entice capital away from others thought to carry greater political and economic risk. For instance, political unrest can result in a decline in the value of a currency and a capital flight to currencies in more stable nations.
Final Note on factors affecting forex market
The real return of a portfolio is based on the exchange rate of the currency in which the majority of its assets are held. It goes without saying that a dropping exchange rate reduces the buying power of income and capital gains from any returns. Additionally, other income considerations like interest rates, inflation, and even capital gains from local stocks are impacted by the exchange rate. Investors should nevertheless have some awareness of how currency values and exchange rates play a significant influence in the rate of return on their assets, even if exchange rates are determined by multiple complicated factors that frequently confound even the most knowledgeable economists.

Visit us on: www.milliva.com